Intro to DevOps: CI/CD Essentials for High-Performing Tech Teams
Modern software delivery is no longer defined by speed alone. It is defined by reliability, repeatability, and the ability to adapt without breaking production systems. DevOps emerged as a response to these demands, and at the center of DevOps lies Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery, commonly referred to as CI/CD. These practices form the operational backbone of high-performing technology teams, enabling faster releases, higher quality software, and stronger collaboration between development and operations. Todays article introduces the core principles of DevOps with a focused exploration of CI/CD essentials. It explains how CI/CD works, why it matters, and how tech teams can implement it effectively to support scalable and resilient software delivery.
Table of Contents
- DevOps Foundations and the Rise of CI/CD
- What CI/CD Really Means
- Continuous Integration Explained
- Continuous Delivery and Deployment
- Core Components of a CI/CD Pipeline
- Popular CI/CD Tools and Platforms
- Business and Team Impact of CI/CD
- CI/CD Best Practices for Tech Teams
- Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- The Future of CI/CD in DevOps
- Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
- Resources
DevOps Foundations and the Rise of CI/CD
DevOps is not a toolset or a job title. It is a cultural and operational model that breaks down silos between development, operations, and quality assurance. Traditional software delivery relied on long release cycles, manual handoffs, and late-stage testing. This approach increased risk and slowed innovation. CI/CD emerged as a response to these inefficiencies. By automating code integration, testing, and deployment, CI/CD enables teams to release small changes frequently instead of large, risky updates. Research from the DevOps Research and Assessment group consistently shows that teams practicing mature CI/CD deploy code up to 208 times more frequently and recover from failures significantly faster than low-performing teams.
What CI/CD Really Means
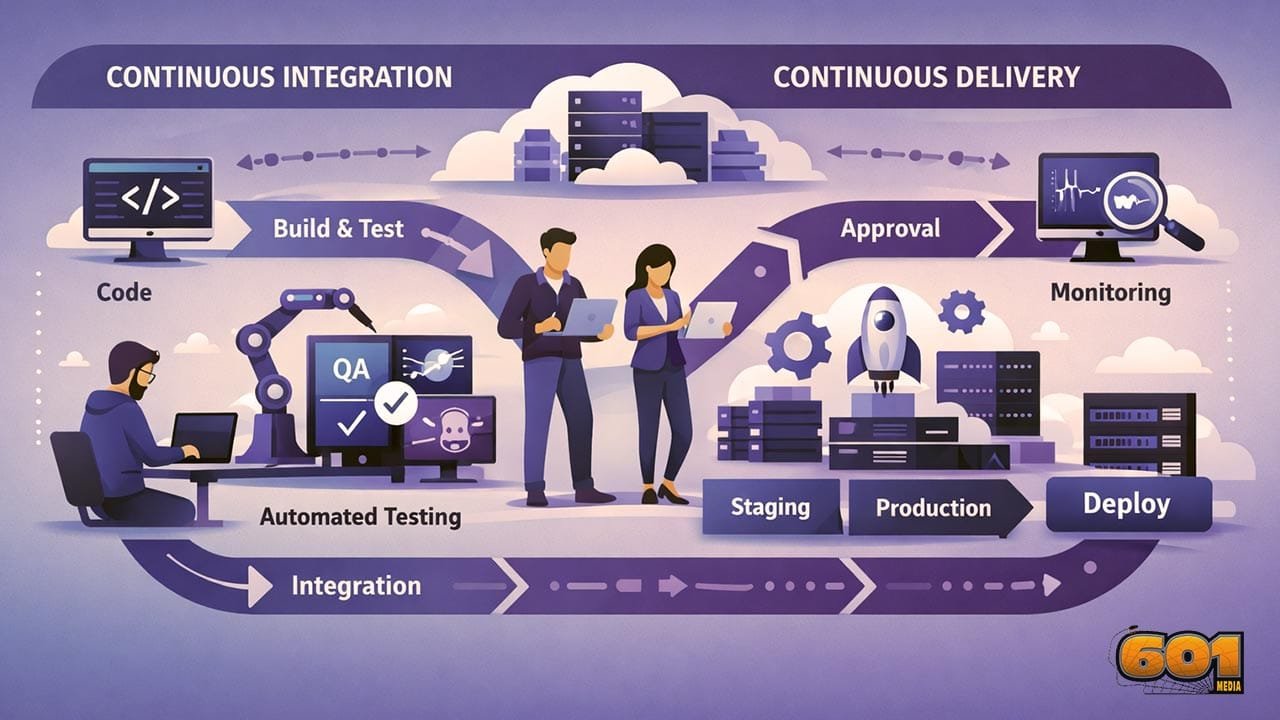
CI/CD is often discussed as a single concept, but it consists of two distinct yet interconnected practices. Continuous Integration focuses on merging code changes into a shared repository frequently. Each change is automatically tested to detect errors early. Continuous Delivery ensures that validated code is always in a deployable state. Continuous Deployment goes one step further by automatically releasing changes into production once all checks pass. Together, these practices reduce integration issues, improve code quality, and create a predictable release process.
Continuous Integration Explained
Continuous Integration begins when developers commit code changes to a version control system. Automated build processes compile the code and execute test suites. If any test fails, the pipeline stops, alerting the team immediately. The key value of CI lies in fast feedback. Bugs are detected minutes after being introduced instead of weeks later. This significantly reduces the cost and complexity of fixes. High-performing teams typically integrate code multiple times per day. This practice encourages smaller, focused changes that are easier to review, test, and maintain.
Continuous Delivery and Deployment
Continuous Delivery extends CI by automating the steps required to prepare software for release. This includes additional testing, security scans, and packaging processes. In Continuous Delivery, deployment to production requires manual approval. In Continuous Deployment, the release happens automatically. The choice between the two depends on risk tolerance, regulatory requirements, and organizational maturity. Both approaches eliminate last-minute release stress and allow teams to deliver features on demand rather than on fixed schedules.
Core Components of a CI/CD Pipeline
A CI/CD pipeline consists of several interconnected components. Version control systems manage code changes and collaboration. Build automation compiles and packages applications. Automated testing validates functionality, performance, and security. Deployment automation moves applications across environments consistently. Monitoring and logging close the feedback loop by providing real-time insights into application health and user impact. Each component reinforces reliability and reduces human error, which is one of the primary causes of production failures.
Popular CI/CD Tools and Platforms
CI/CD tooling has evolved rapidly. Platforms such as Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and Azure DevOps offer integrated pipeline management. Cloud-native ecosystems often combine CI/CD with containerization and orchestration technologies. This enables consistent deployments across development, staging, and production environments. Tool selection should align with team skills, infrastructure strategy, and security requirements rather than following industry trends blindly.
Business and Team Impact of CI/CD
CI/CD directly supports business agility. Faster release cycles allow organizations to respond quickly to customer feedback and market changes. Automated quality checks reduce production incidents and improve user trust. From a team perspective, CI/CD reduces burnout by eliminating manual release work and late-night deployments. Engineers spend more time solving meaningful problems and less time firefighting. Organizations adopting CI/CD often report measurable improvements in deployment frequency, lead time, and system stability.
CI/CD Best Practices for Tech Teams
Successful CI/CD implementation requires discipline and consistency. Pipelines should be treated as production systems, versioned and reviewed like application code. Tests must be reliable and fast. Slow or flaky tests undermine confidence and slow delivery. Security checks should be integrated early rather than added as a final gate. Most importantly, CI/CD should be supported by a strong DevOps culture that values collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Teams often struggle with legacy systems, resistance to change, and pipeline complexity. Incremental adoption is key. Start by automating builds and tests before expanding into full delivery pipelines. Clear ownership and shared responsibility prevent pipelines from becoming neglected or fragile. Regular reviews help ensure pipelines evolve alongside the product. Training and internal advocacy play a critical role in sustaining long-term success.
The Future of CI/CD in DevOps
CI/CD continues to evolve with advancements in artificial intelligence, infrastructure automation, and platform engineering. Intelligent test selection, automated rollback strategies, and policy-driven pipelines are becoming standard. As software systems grow more complex, CI/CD will remain essential for managing risk and maintaining velocity. Teams that invest in CI/CD today are better positioned to scale tomorrow.
Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
CI/CD is not merely a technical upgrade. It is a strategic capability that transforms how teams build, test, and deliver software. By embracing CI/CD essentials, tech teams gain speed without sacrificing stability, autonomy without chaos, and innovation without burnout. In a competitive digital landscape, CI/CD is no longer optional. It is foundational.
Resources
- Accelerate: The Science of Lean Software and DevOps
- State of DevOps Reports by DORA
- Continuous Delivery by Jez Humble and David Farley
- Google Cloud DevOps Research
I am a huge enthusiast for Computers, AI, SEO-SEM, VFX, and Digital Audio-Graphics-Video. I’m a digital entrepreneur since 1992. Articles include AI assisted research. Always Keep Learning! Notice: All content is published for educational and entertainment purposes only. NOT LIFE, HEALTH, SURVIVAL, FINANCIAL, BUSINESS, LEGAL OR ANY OTHER ADVICE. Learn more about Mark Mayo